- Singh Biome Lab
- Research
- Shiga-toxin Producing E. coli
Shiga-toxin Producing E. coli
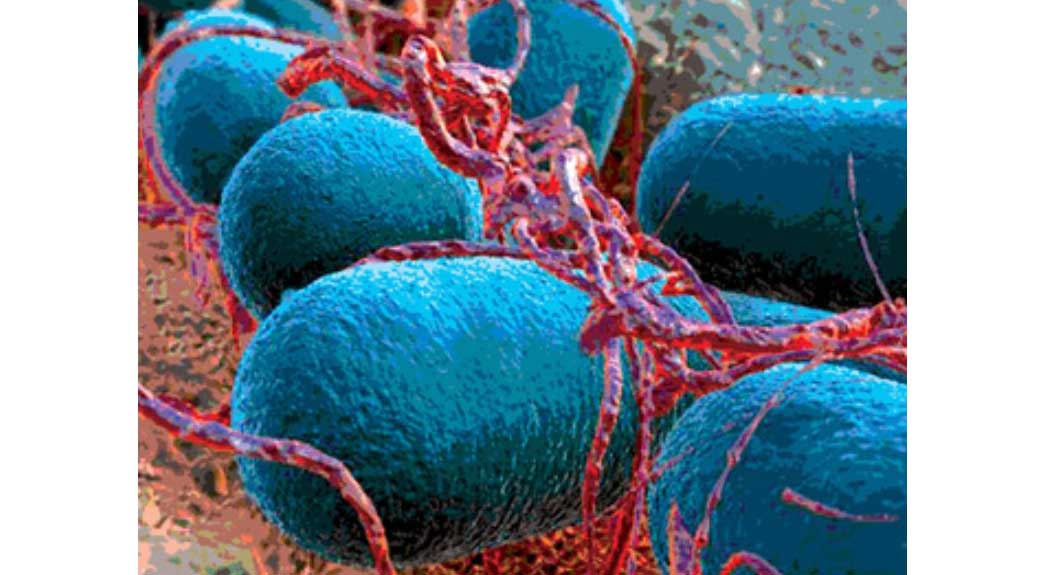
Shiga toxin producing E. coli (STEC) is a major foodborne pathogen with significant public health importance in the United States and around the world. STEC are reported to survive in the complex gut of livestock which serve as reservoir host resulting in transfer of this pathogen from from farm to fork. Biofilm formation is one mechanism employed by this pathogen for survival and pathogenesis. We therefore aim at elucidating role of biofilm formation in STEC colonization and persistence. For this we are working with isolates from various sources including clinical isolates. Preventative strategies that target biofilm formation may be pertinent for one health especially human health. In addition our studies will focus on STEC biofilm formation under conditions that mimic host gut, and investigate genes expressed under these conditions including shiga-toxin.
Contact
Singh Biome Lab
Department of Biological Sciences
Montgomery Hall 359
815-753-7839
psingh1@niu.edu