Corrective/Preventive Actions
During the monitoring process, if any problems or deviations from established procedures are observed, then they should be investigated to find the source of the problems and take appropriate corrective actions. However, the process of finding the root cause of a problem may at times be difficult due to the complex nature of environmental problems and the multiplicity of factors contributing to them.
One of the techniques used for finding root causes of problems is the “root-cause map” or the “fishbone diagram”. The root-cause map is a brainstorming technique for identifying and discussing possible major causes of a problem and the potential root causes for each of those categories. The example shown in the figure illustrates the root-cause map for an air quality degradation problem. The effect or the outcome is shown in the box on the right as the head of the “fish” and the major categories of causes and the root causes for each of those causes are shown on the “fishbone” in the diagram.
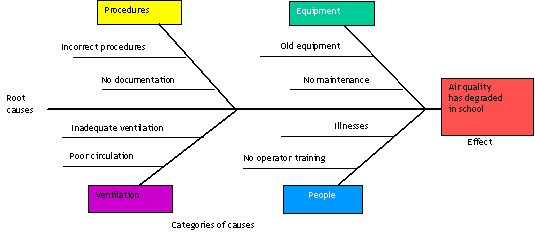
After the root-cause map has been drawn for a given problem, the team should discuss each of the root causes and the actual cause contributing to the effect should be identified. Once a problem has been identified, appropriate corrective measures should be taken to correct the problem and prevent it from occurring again. For this purpose, new operational procedures may have to be developed or existing procedures may have to be revised, and documented. Personnel responsible for implementing the procedures should also be trained and the entire process should be monitored.
|


